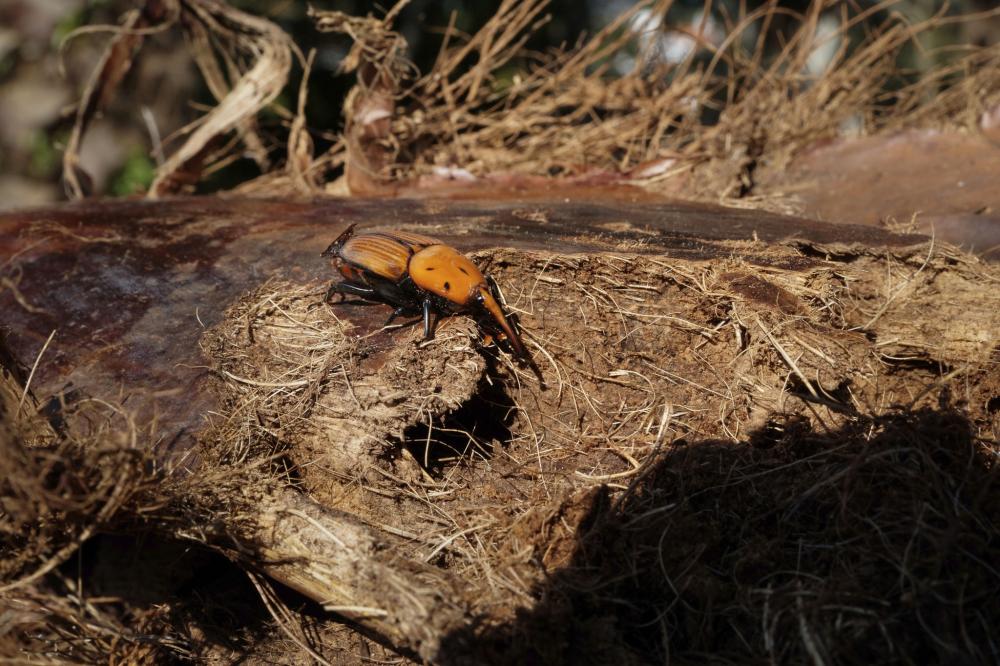

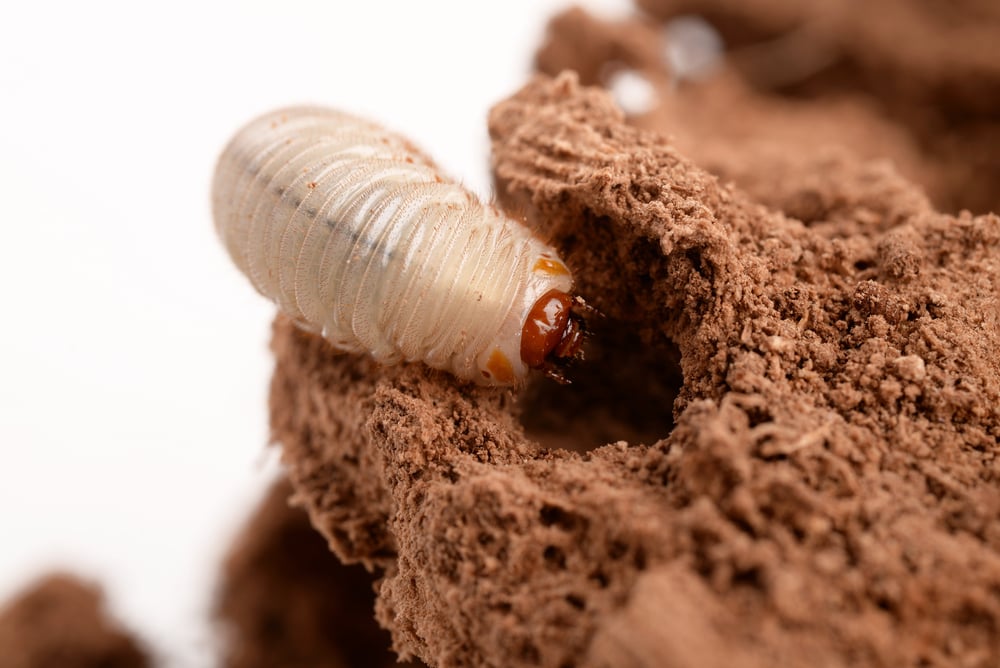
- The red palm weevil is a very dangerous insect that infests palm trees and feeds on the internal tissues of the trunk , leading to the tree weakening and gradual death if not treated early.
- Its scientific name is Rhynchophorus ferrugineus , and it is known for its reddish-brown color and length of 2.5 to 3.5 cm . It has a long proboscis which the female uses to drill holes inside the trunk to lay eggs . From here, the infestation begins, and the larvae hatch and live inside the trunk, feeding on the soft tissues without being seen. For this reason, it is considered one of the most dangerous hidden pests of palm trees.
⚠️ Risk of injury
- A single female lays up to 300 eggs inside the trunk.
- The larvae feed inside the palm tree and weaken it from within without any obvious symptoms appearing at first.
- It spreads between farms through infected offshoots or contaminated pruning tools .
- It thrives in hot and humid climates, especially in coastal areas and oases.
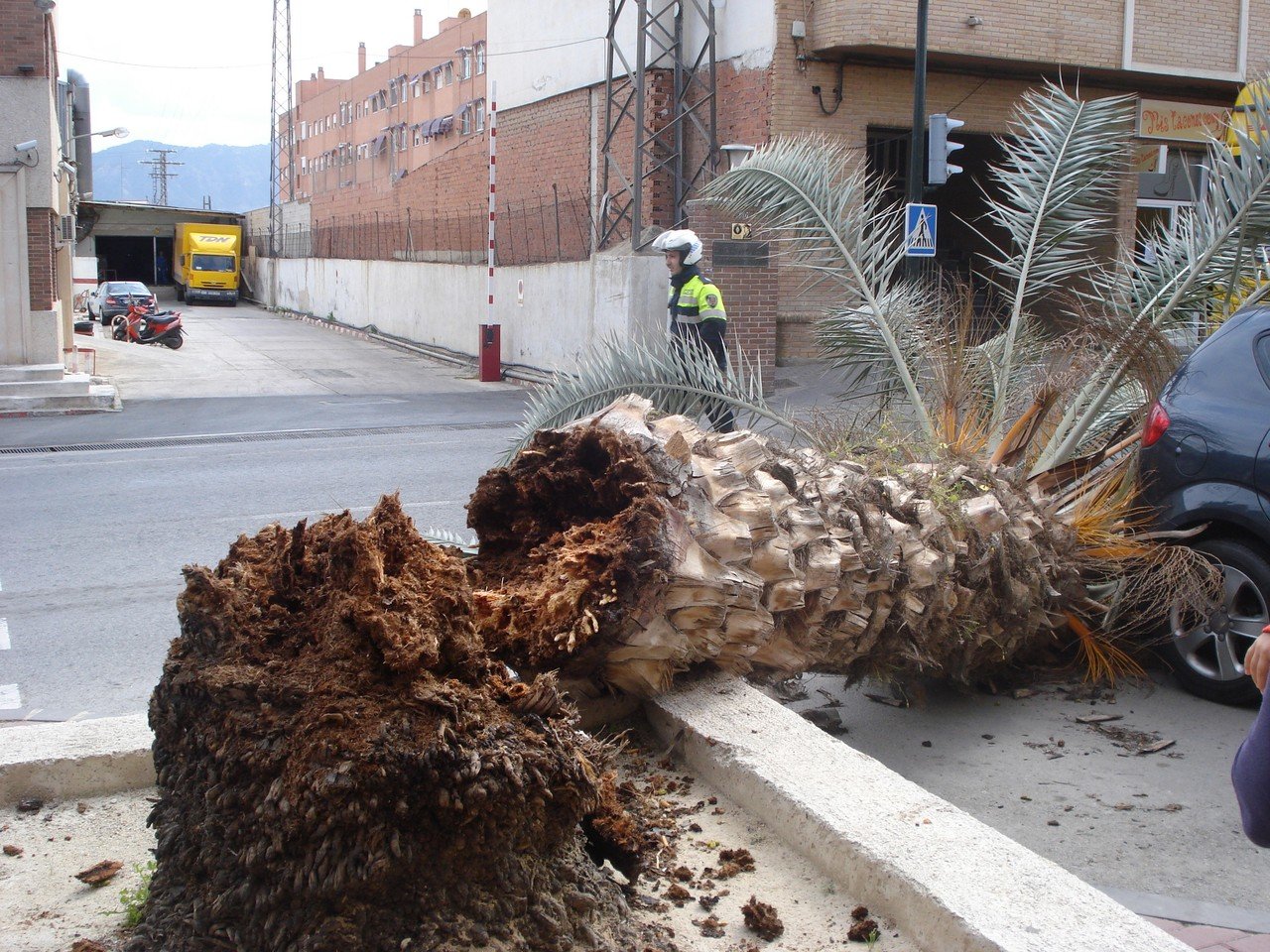

Symptoms of infection
- A sticky brown or yellow sap comes out of the holes in the trunk.
- There is a foul fermenting smell coming from inside the trunk.
- Wilting and easy shedding of the middle fronds .
- Note: Brown sawdust or insect droppings under the palm tree.
- Hearing a digging or gnawing sound from inside the trunk when the ear is brought close.
- Bending or breaking of the trunk in severe injuries.
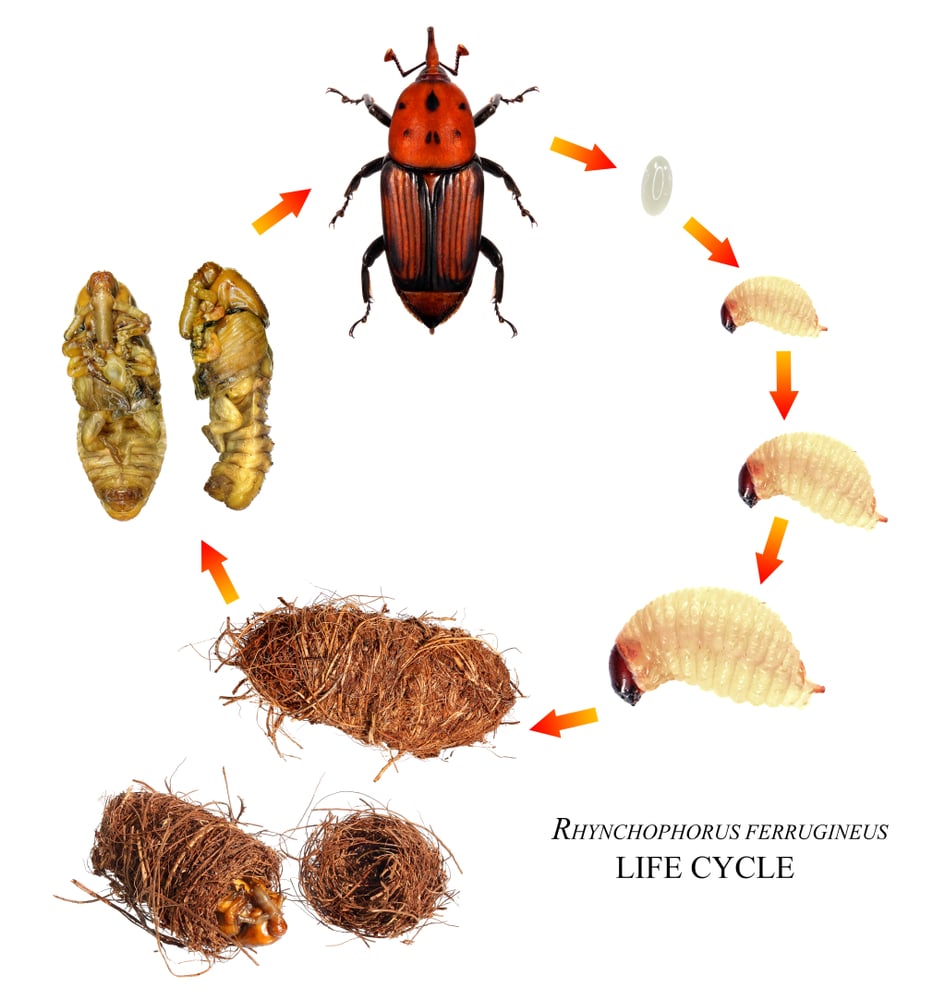
🔄 The life cycle of the palm weevil
- The insect goes through four main stages:
- Eggs: Placed inside wounds, they hatch within 2–5 days.
- Larva: The most dangerous stage, it feeds on internal tissues for 25–60 days.
- The pupa: transforms inside cocoons of palm fibers for 10–20 days.
- The adult insect: lives for up to 3 months and begins a new cycle of reproduction.
- ⏳ The complete cycle takes 60 to 90 days , allowing for the emergence of several generations in a single year.
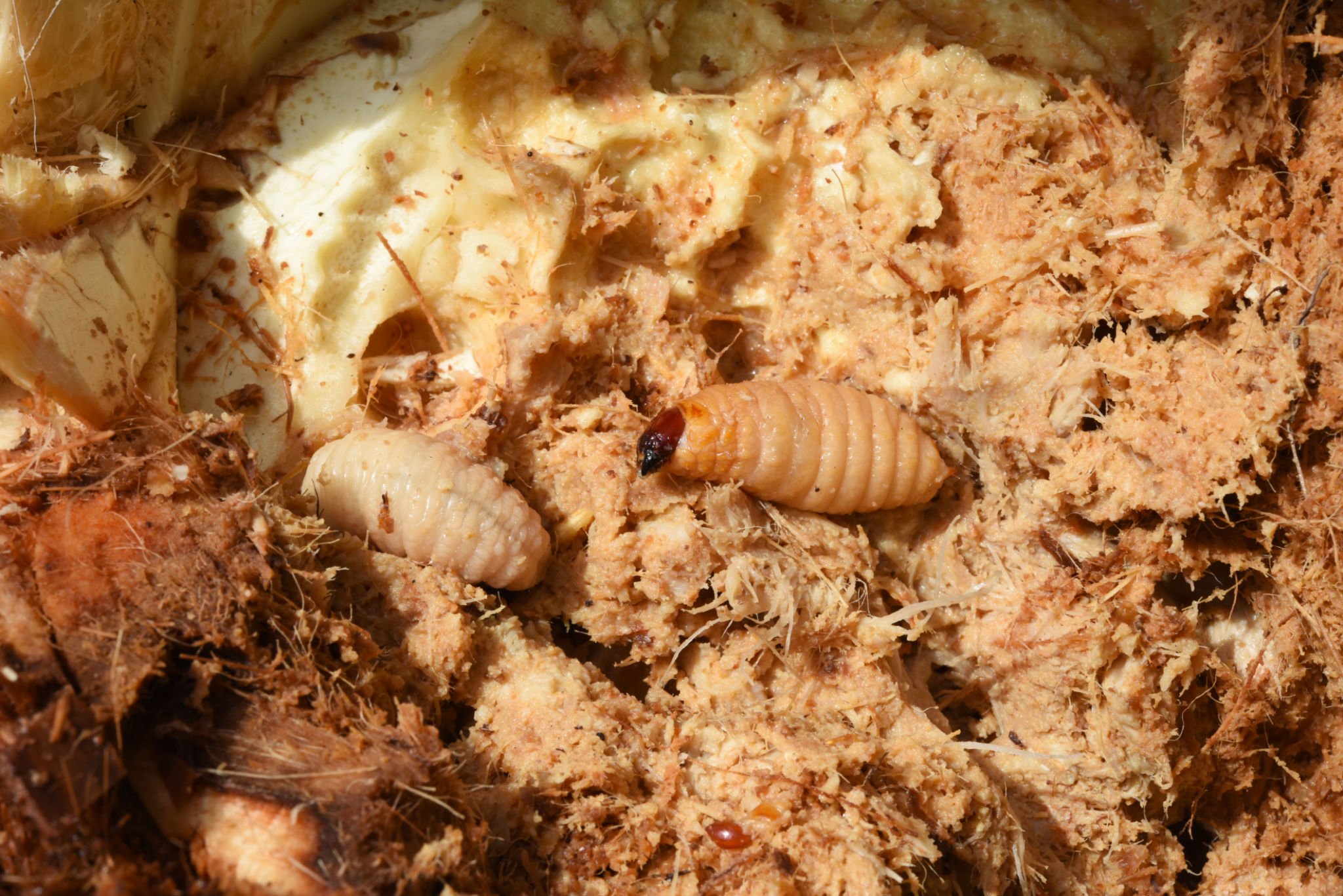

🌴 Damage to palm trees
- Erosion of the internal tissues of the trunk and general weakness of the tree.
- Growth stopped, the crown dried out, and the fronds fell off.
- The young shoots die within weeks.
- Date production has decreased by up to 70% in affected farms.
🧩 Early detection
- Installing pheromone traps (Ferrolure) to detect the first appearance of the insect.
- Check the base of the fronds and new shoots weekly.
- Using acoustic detection devices in large projects.
- Monitor the sap coming out of the trunk for any change in color or smell.
🛠️ Prevention and control methods
- 🌿 First: Prevention
- Examine the seedlings thoroughly before planting.
- Sterilize pruning tools after each use.
- Painting the trunk after cleaning:
- After removing the dry fronds and cleaning the base of the palm tree, the lower part of the trunk should be coated with a preventative pesticide to prevent weevils from entering or laying eggs inside the cracks.
- It is used for this purpose:
- Chlorpyrifos 48% at a rate of 15 ml per 1 liter of water .
- Fipronil 5% at a rate of 5 ml per 1 liter of water .
- It is sprayed or painted onto the trunk up to a height of 50 cm, and the process is repeated every two months or after pruning.
- Dispose of dead, burned, or deeply buried palm trees.
- Install pheromone traps every 10 acres to monitor the presence of the insect.

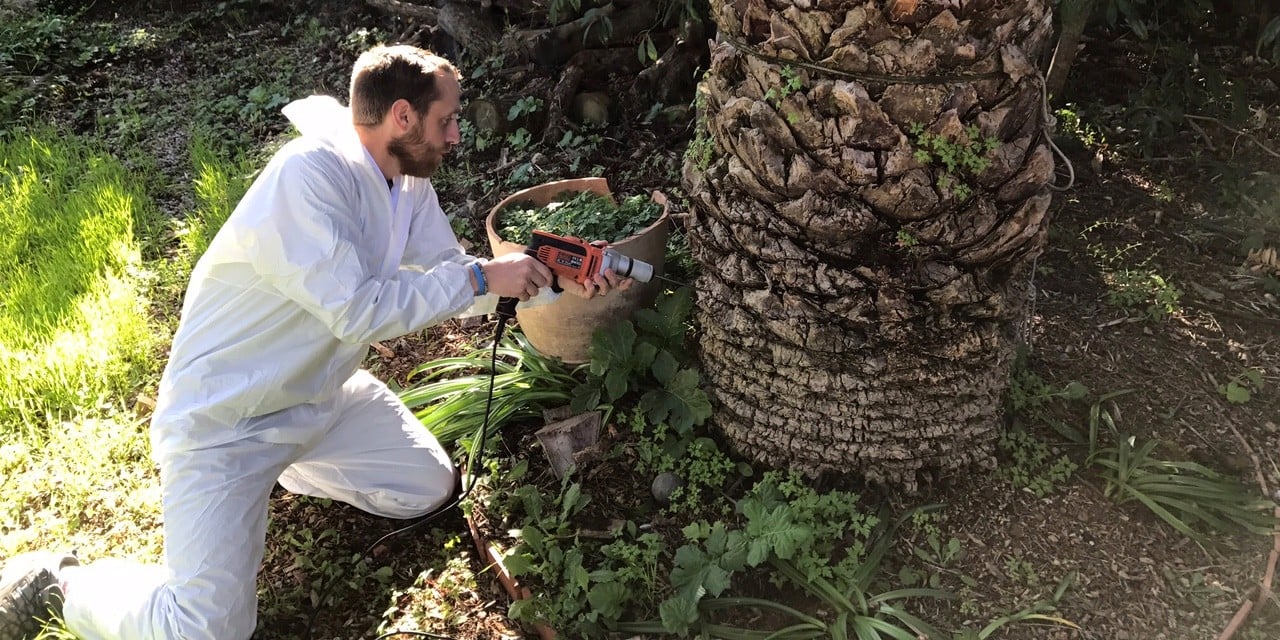
💊 Second: Chemical control
- When an infection appears, the following materials are recommended:
- Imidacloprid (35%) at a rate of 10 ml per 1 liter of water , injected into the trunk or base of the palm.
- An effective systemic insecticide that travels through the sap and kills the insect from within.
- Chlorpyrifos (Chlorpyrifos 48%) at a rate of 15 ml per 1 liter of water , sprayed or injected into active holes.
- Fast acting and effective against the complete phases.
- Thiamethoxam (25%) at a rate of 8 ml per 1 liter of water , for injection or topical spraying.
- Its effect is long-lasting and eliminates the insect and larvae inside the trunk.
- Abamectin (1.8%) at a rate of 5 ml per 1 liter of water , injected into the active bores.
- It causes paralysis and rapid death of the insect.
- Fipronil (5%) at a rate of 5 ml per 1 liter of water , spray around the base of the palm tree and on the trunk.
- Effective against the adult insect and its mobile stages.
⏳ The treatment is repeated every 30 days until the infection stops.

⚙️ Third: Precautions during treatment
- Seal the injection holes immediately with agricultural paste or paraffin wax.
- Do not mix different pesticides without technical advice.
- Prepare pesticides using only fresh water.
- Perform the injection or spraying in the early morning or before sunset to reduce evaporation.
🌴 Tips for farmers
- Check the palm trees regularly and do not neglect the first signs.
- Do not transport seedlings from infested areas.
- Keep a record of your examination and treatment appointments.
- If you suspect an injury, consult a qualified engineer or technician.
- Regular prevention is cheaper and better than treatment after it's too late.

