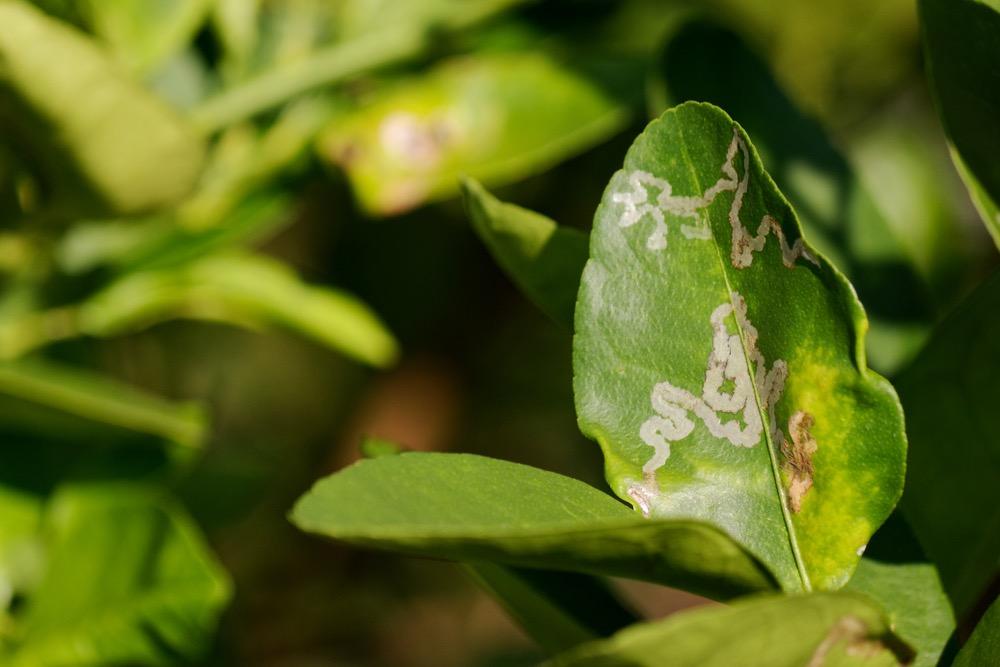

- Leaf miners or leaf borers are among the most common pests in vegetable, flower, and fruit crops.
- The larvae feed inside the leaf tissue, forming winding tunnels that distort the leaves and weaken the plant.
- Its danger increases in greenhouses and warm areas, where it multiplies rapidly and causes significant losses in production.
The types commonly found in the Kingdom include:
- Liriomyza trifolii (tomato tunnel maker) – spreads in greenhouses.
- Liriomyza sativae (vegetable tunnel maker) – spreads in open fields and tolerates high temperatures.
- These species are widespread in most regions of the Kingdom, especially Qassim, Riyadh, Jeddah and Taif , and are considered among the most dangerous pests of protected vegetables.
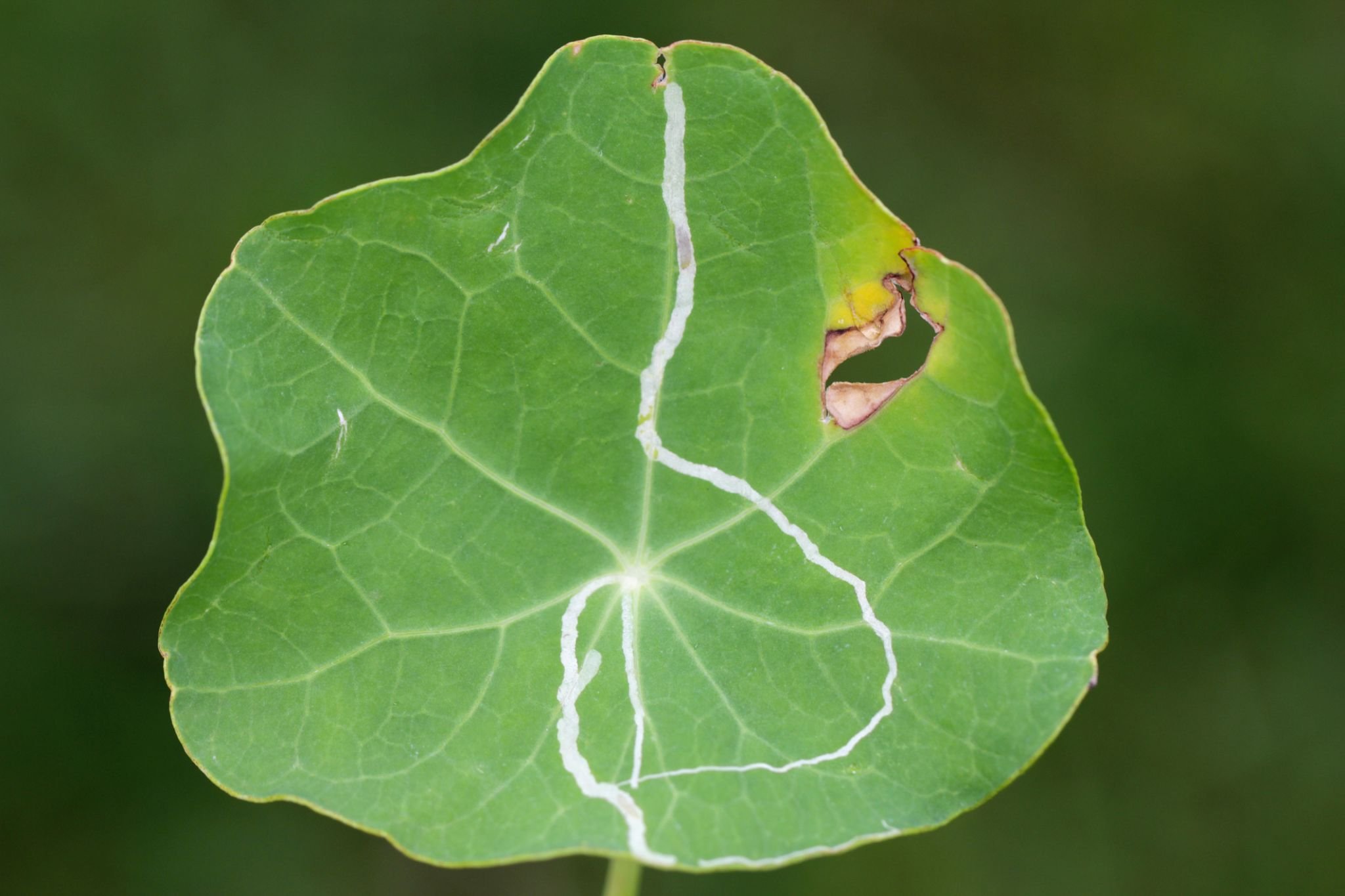

🔍 Symptoms of infection
- Plant infestation by leaf miners can be identified by the following signs:
- The appearance of silver or white wavy lines within the leaf tissue.
- The presence of small black spots (larval droppings).
- The leaves gradually turn yellow and dry out .
- General weakness in the plant and delayed growth or flowering.
- In severe cases, leaf drop and crop yield decrease by more than 50% .
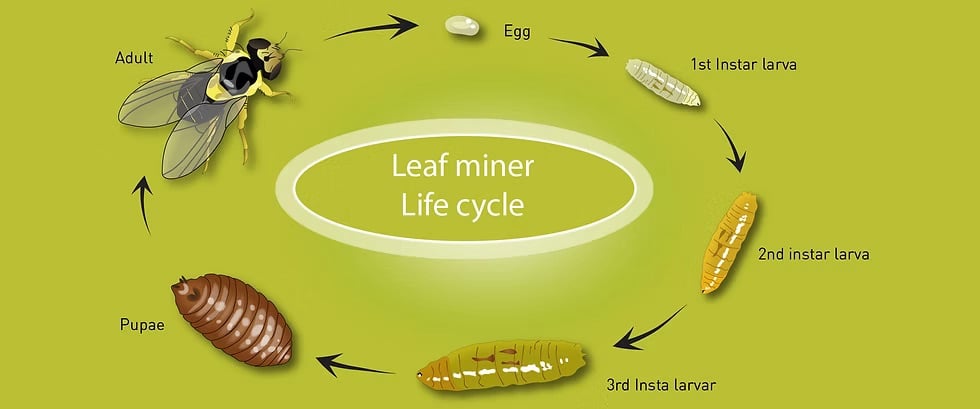
🔄 Insect life cycle
- The insect goes through four stages:
- Eggs: The female lays the eggs inside the leaf, and they hatch within 2-3 days.
- The larva: It burrows tunnels inside the leaf and feeds on plant sap.
- The pupa: The larva transforms in the soil or on the leaf within 5-7 days.
- The adult insect: a small fly that lives for about two weeks and begins a new cycle.
- 🔁 In hot weather, the insect can complete 3 to 4 generations per month .
🌾 Crops susceptible to infection
- Tomatoes 🍅
- Cucumber 🥒
- Beans and peas 🌿
- Potatoes 🥔
- Onions 🧅
- Flowers and ornamental plants 🌸
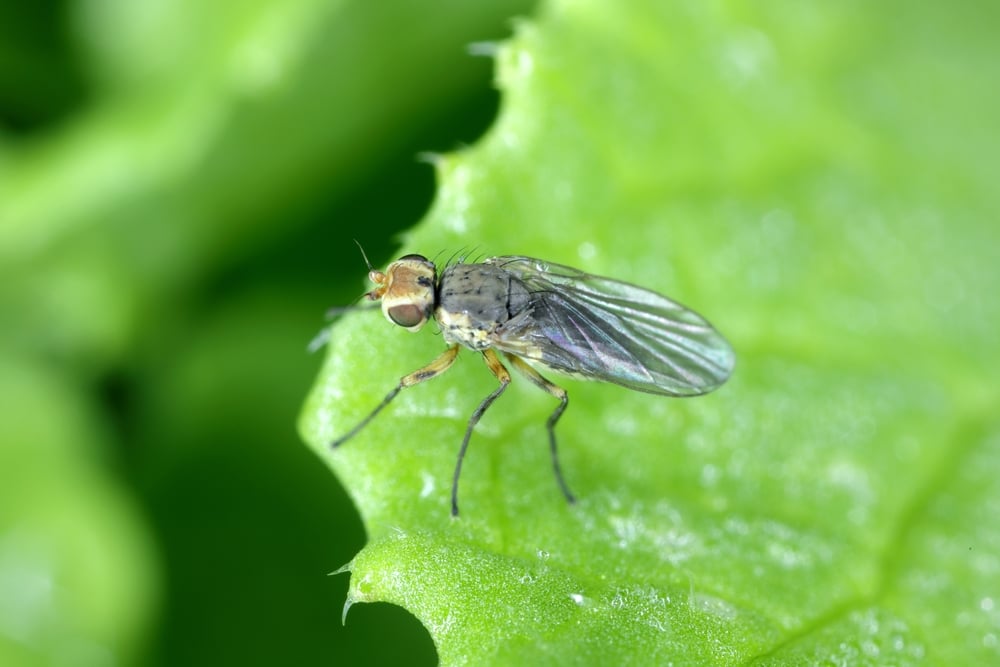

💥 Damage to the plant
- Reduced efficiency of photosynthesis.
- Poor growth and premature leaf drop.
- Plant appearance is distorted and crop quality is reduced.
- Increased chance of fungal infection due to dehydration.
🛠️ Prevention and control methods
- 🌱 First: Agricultural control
- Remove infected leaves early and burn them outside the farm.
- Use insect-proof netting (Mesh 50) in greenhouses.
- Install yellow sticky traps to monitor the adult insect.
- Avoid excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers.
- Improve ventilation and reduce humidity.
- Examine the seedlings thoroughly before planting.
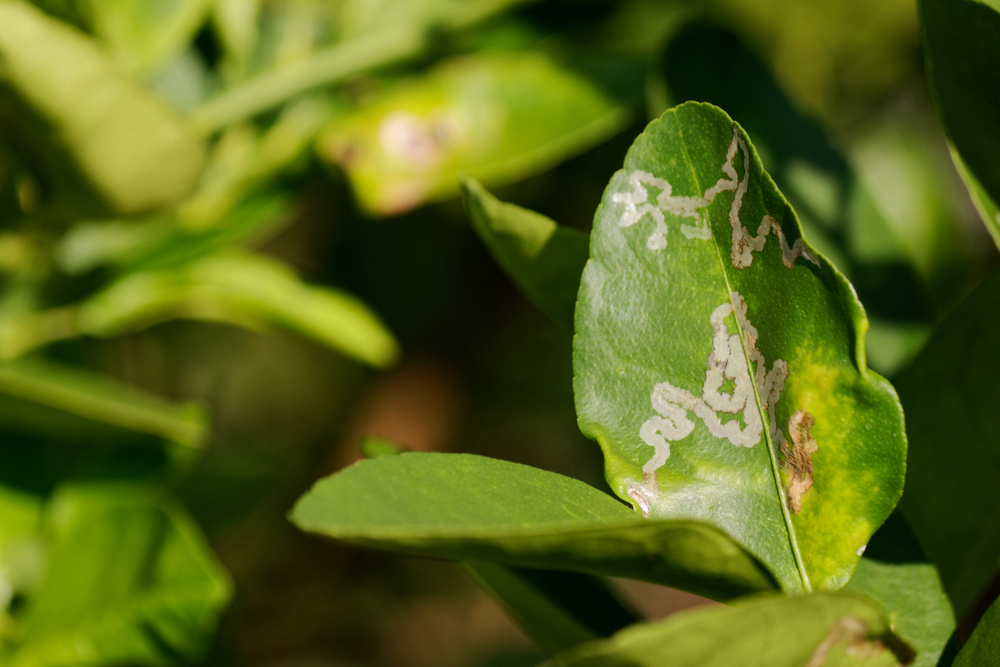

💊 Second: Chemical control
- When an infestation occurs, effective translaminar or systemic pesticides are used to reach the larvae inside the leaf.
- The active ingredients should be alternated to avoid resistance.
- 🔹 Spinosad (Spinosad 24%)
- Dosage: 0.3 – 0.6 ml per 1 liter of water.
- Function: It penetrates the leaf and eliminates the larvae inside the tunnels.
- Safety period: 3-5 days.
- 🔹 Abamectin (1.8%)
- Dosage: 0.5 – 1 ml per 1 liter of water.
- Function: It causes rapid paralysis of the insect and stops it from feeding.
- Safety period: 5-7 days.
- 🔹 Cyantraniliprole (Cyantraniliprole 20%)
- Dosage: 0.8 – 1.2 ml per 1 liter of water.
- Function: A modern pesticide from the diamide group, it disrupts muscles and stops movement immediately.
- Features: Safe for biological enemies, long-lasting (up to 14 days).
- Safety period: 7 days.
- 🔹 Imidacloprid (35%)
- Dosage: 0.5 – 1 ml per 1 liter of water.
- Function: Systemic insecticide and preventative against sucking insects and leaf miners.
- Safety period: 10 days.
- ⏱️ Spraying frequency: Every 10-12 days depending on the severity of the infestation.
🌿 Orchid's advice for farmers
- Because the leaf miners live inside the leaf tissue, they cannot be eliminated by surface spraying alone.
- Therefore, we recommend using penetrating or systemic pesticides with alternation between active ingredients.
- Make sure to monitor the crop regularly, and always check the lower leaves, because early detection is the key to successful control .

